Primary Immunodeficiencies
Description
Last update: October 1st, 2019
Primary Immunodeficiency (PID) disorders comprise a heterogeneous group of inherited conditions usually diagnosed during infancy or childhood. They are extremely diverse in their underlying causes, with over 300 individual mutations described so far. As a result of such mutations, one or more components of either the adaptive or innate immune response might be impaired, resulting in the immune system being unable to effectively fight infections and other diseases. There are different classification criteria (e.g. ESID, IUIS, etc.) but most of the immunodeficiencies can be grouped attending to their etiology:
- Antibody deficiencies
- Cellular deficiencies
- Combined cellular and antibody deficiencies
- Phagocytic cell deficiencies
- Complement deficiencies
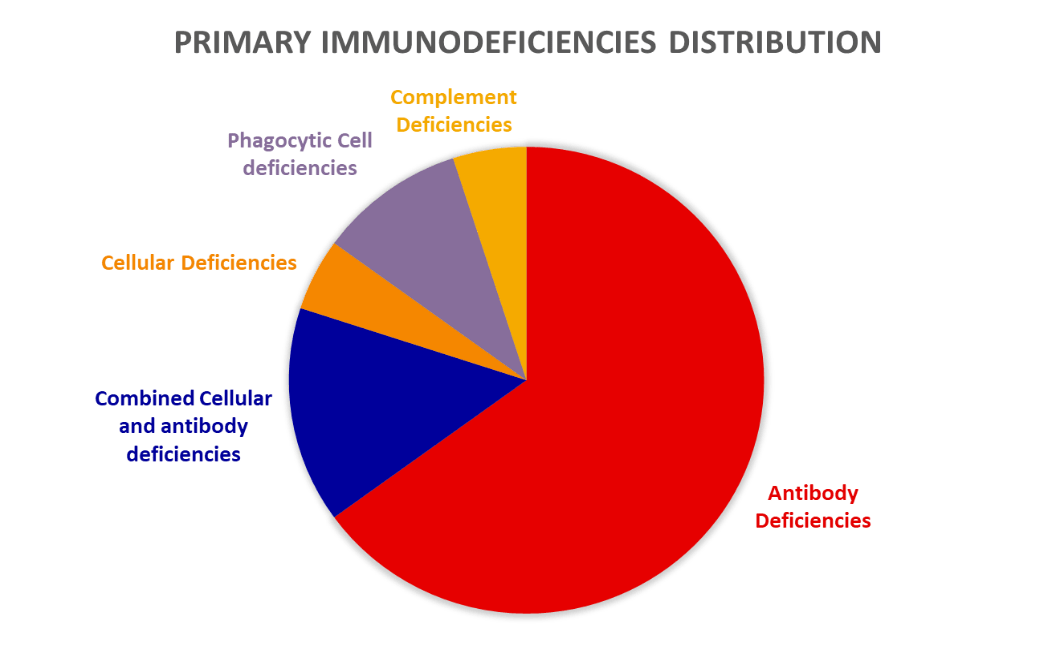
Adapted from Jones A; Immunological disorders in infants & children, 5th edition, Archives of Disease in Childhood 2005;90:549.
Resources
Publications:
- Bousfiha A, et al. The 2017 IUIS Phenotypic Classification for Primary Immunodeficiencies. J Clin Immunol. 2018 Dec;38(1):129-43. Go to publication
- Raje N, Dinakar C. Overview of Immunodeficiency Disorders. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2015 Nov;35(4):599-623. Go to publication
- Jones A. Immunological disorders in infants & children, 5th edition. Archives of Disease in Childhood. 2005;90:549. Go to publication




