Plasma Cell Dyscrasias
Description
Last update: October 1st, 2019
Plasma Cell Dyscrasias (PCD) are a heterogeneous group of disorders characterized by bone marrow infiltration with monoclonal plasma cells and the presence of immunoglobulin in the serum.
The international Myeloma Working Group (IMWG) has defined diagnostic criteria for PCD:
- Monoclonal Gammopathy of Undetermined Significance (MGUS)
- Smoldering (Asymptomatic) Plasma Cell Myeloma (SMM)
- Multiple Myeloma (MM)
Other plasma cell dyscrasias are plasma cell leukemia (PCL), plasmacytoma and primary amyloidosis.
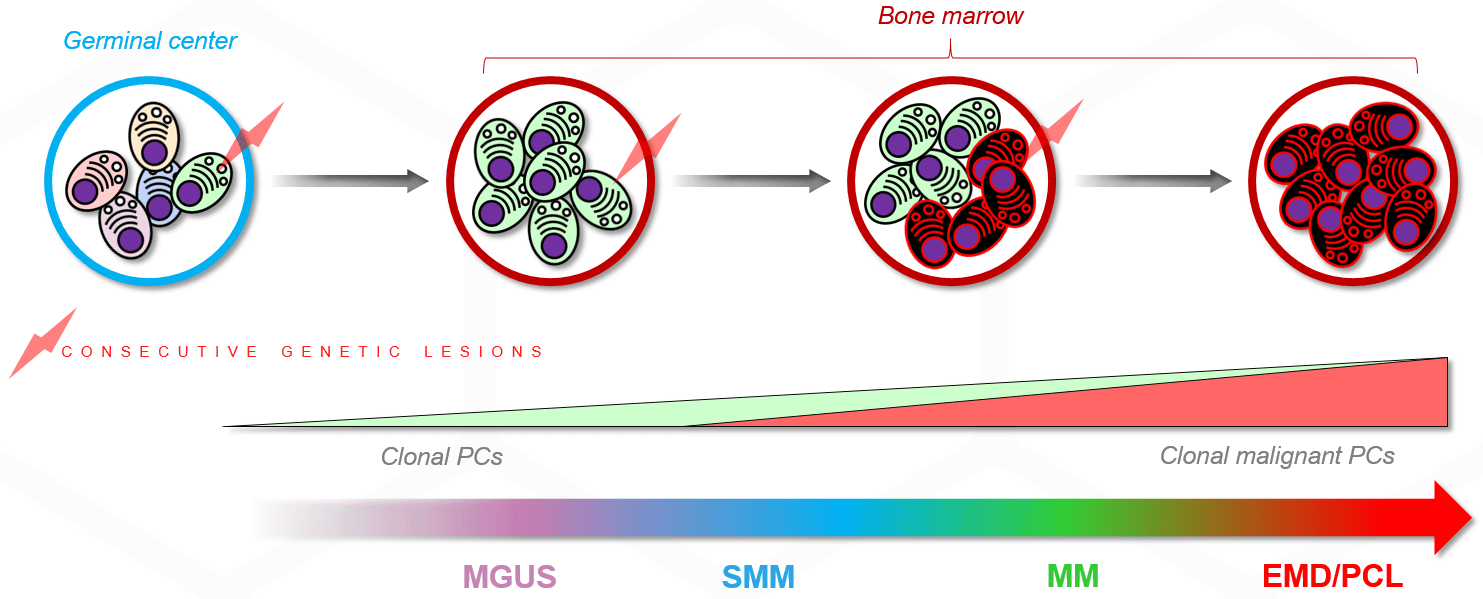
Monoclonal Gammopathy of Undetermined Significance (MGUS)
Premalignant plasma cell disorder which can sometimes progress to more serious diseases (around 1% per year). As a benign condition, MGUS does not require treatment but it does require regular check-ups. The presence of circulating plasma cells detected by a sensitive method is a predictor of progression in MGUS.
- Concentration of serum monoclonal protein (M-protein) < 3 g/dL and;
- Bone marrow with < 10 % monoclonal plasma cells and;
- Absence of anemia, hypercalcemia, renal failure or end-organ damage related to the proliferative progress
Smoldering (Asymptomatic) Plasma Cell Myeloma (SMM)
Asymptomatic plasma cell disorder considered to intermediate between MGUS and MM. SMM has a higher risk of progression to malignancy (around 10%-20% per year). As a benign condition, SMM does nor require treatment but it does require regular check-ups. The presence of circulating plasma cells detected by a sensitive method is a predictor of progression in SMM.
- Concentration of serum monoclonal protein (M-protein) ≥ 3 g/dL or;
- Urinary monoclonal protein ≥ 500 mg/24 h and/or;
- Bone marrow monoclonal plasma cells from 10%-60% and;
- Absence of anemia, hypercalcemia, renal failure or end-organ damage related to the proliferative progress nor amyloidosis.
Multiple Myeloma (MM)
Blood cancer arising from abnormal plasma cells which multiply and spread within the bone marrow. It can affect multiple places in the body such as the spine, skull, pelvis and other active areas in a bone marrow of an adult. Patients are diagnosed with MM usually over the age of 65. Myeloma is considered as an incurable cancer but several efforts are being made to improve treatments and the expectancy of life has increased greatly in the last 10 years.
- Bone marrow monoclonal plasma cells ≥ 10% or;
- Biopsy-proven medullary or extramedullary plasmacytoma and;
- Any of the following myeloma defining events:
- Evidence of end-organ damage attributed to underlying plasma cell proliferation (e.g. hypercalcemia, renal insufficiency, anemia and bone lesions).
- Bone marrow monoclonal plasma cells ≥ 60% and;
- Uninvolved serum free light chain ratio ≥ 100;
- >1 focal lesion on MRI studies
Resources
Publications:
- Rajkumar SV, et al. International Myeloma Working Group updated criteria for the diagnosis of multiple myeloma. The Lancet Oncology. 2014 Nov;15(12):538-48. Go to publication
- Soh KT et al. Diagnosis of Plasma Cell Dyscrasias and Monitoring of Minimal Residual Disease by Multiparametric Flow Cytometry. Clin Lab Med. 2017 Dec;37(4):821-53. Go to publication




